Patient duplicates and data integrity in Electronic Medical Records represent far more than an administrative inconvenience—they constitute a genuine threat to patient safety and healthcare quality. When the same individual exists multiple times within a healthcare system, their medical history becomes fragmented across different records, creating dangerous gaps in clinical understanding. Healthcare providers may unknowingly duplicate treatments, miss critical allergies or contraindications, or fail to recognize patterns in a patient’s care history. These scenarios can lead to medication errors, unnecessary procedures, and compromised treatment decisions that directly impact patient outcomes.
The financial implications are equally significant. Duplicate records inflate administrative costs, create billing complications, and reduce operational efficiency across healthcare organizations. Staff spend valuable time reconciling conflicting information, while the integrity of health data analytics and population health initiatives suffers from inaccurate patient counts and scattered clinical data.
Recognizing these challenges, the Tamanu EMR has developed a comprehensive, multi-layered approach to patient deduplication that addresses both prevention and remediation. This systematic strategy ensures that healthcare providers can maintain clean, accurate patient databases while delivering safe, coordinated care.
At the centre of any patient management strategy of course, are good processes and procedures, implemented by diligent staff. Tamanu can only help – we recognise though that it is the people at the heart of the system who determine its success.
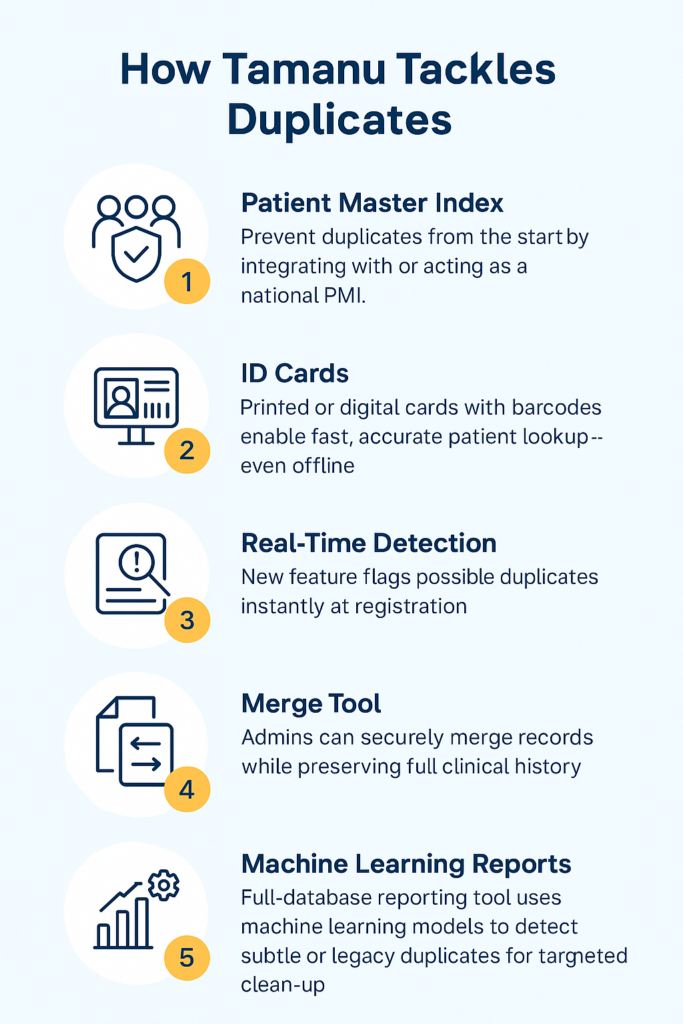
The five Tamanu strategies for de-duplication
Strategy 1: Patient Master Index Integration
The foundation of effective duplicate prevention lies in establishing a unified patient identity management system through a Patient Master Index (PMI) integration. A PMI serves as the authoritative source for patient identities across an entire healthcare network, maintaining a single, comprehensive registry of all patients served by the organization.
Tamanu’s PMI integration offers remarkable flexibility to accommodate diverse healthcare environments. In small to medium sized healthcare systems or those starting fresh, Tamanu can function as the primary PMI, becoming the central repository for patient identities across all connected systems and departments. This approach ensures seamless coordination between different clinical areas, from emergency departments to specialty clinics or allied health, with each patient maintaining a single, consistent identity throughout their care journey.
For larger healthcare networks or those with existing infrastructure investments, Tamanu can consume data from external PMI systems already in operation. This integration capability means organizations don’t need to abandon their current patient identity management investments. Instead, Tamanu synchronizes with these existing systems, ensuring consistency while leveraging established workflows and data governance practices.
Whether consuming data or making it available to other systems, Tamanu achieves this through an HL7 FHIR compliant API, which defines the resources and the business rules around which the data is exchanged.
The PMI approach creates a robust foundation for preventing duplicates at the source. By establishing unique patient identifiers that persist across all systems and encounters, healthcare organizations can eliminate the confusion that arises when patients are known by different identifiers in different departments or facilities.
Strategy 2: ID Card System
Physical patient identification represents a practical, user-friendly solution to many duplicate creation scenarios. Tamanu’s ID card system addresses the common registration challenges that lead to duplicate records—misspelled names, forgotten dates of birth, or variations in how patients provide their personal information.
The system supports both basic ID cards containing essential patient identifiers and more sophisticated photo ID cards that provide visual verification. When patients present their ID cards during registration or subsequent visits, healthcare staff can quickly and accurately retrieve their existing records without relying on potentially inconsistent verbal information. Each ID card contains a barcode, which is scanned in seconds across any part of the health system and all points of care.
This approach proves particularly valuable in busy clinical environments where registration staff may be working under time pressure or dealing with patients who may be distressed, confused, or unable to clearly communicate their details. The ID card system also benefits patients who frequently interact with the healthcare system, creating a streamlined experience that reduces wait times and administrative friction.
Furthermore, the physical ID card serves as a tangible connection between patients and their healthcare records, encouraging patients to maintain and present their identification consistently across different healthcare encounters and providers within the network.
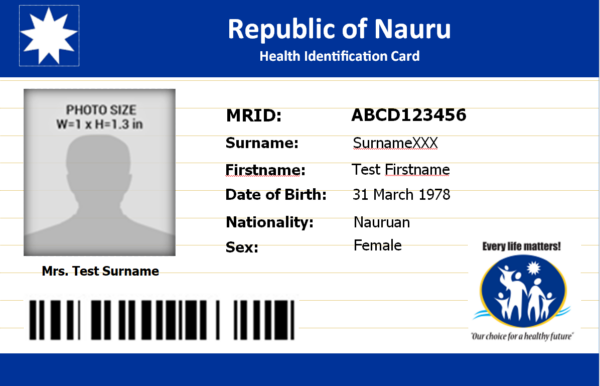
ID cards can be configured for local context and printed directly from Tamanu
Strategy 3: Real-Time Duplicate Detection
Tamanu’s newly released real-time duplicate detection represents a significant advancement in proactive duplicate prevention. This intelligent system operates at the point of patient registration, analyzing incoming patient data against existing records using sophisticated matching algorithms that consider multiple data points simultaneously.
The system evaluates various criteria including name similarities (accounting for common spelling variations and phonetic matches), birth dates, contact information, and other identifying characteristics. This multi-factor analysis helps identify potential duplicates even when exact matches aren’t present, recognizing that patient information may be provided differently across various encounters.
One of the system’s most significant advantages is its offline capability. Many healthcare facilities, particularly in rural or resource-limited settings, face connectivity challenges that can interrupt their workflows. Tamanu’s offline duplicate detection ensures that patient safety measures remain active regardless of internet availability, making it an ideal solution for diverse healthcare environments.
When potential duplicates are identified, the system presents them to registration staff for review, enabling informed decisions about whether to link to an existing record or proceed with creating a new patient entry. This human-in-the-loop approach combines the efficiency of automated detection with the nuanced judgment that healthcare professionals bring to patient identity verification.
Strategy 4: Patient Merge Tool
Despite the best prevention efforts, duplicate records sometimes occur, particularly when integrating legacy data or managing complex patient populations. Tamanu’s patient merge tool provides a secure, comprehensive solution for consolidating duplicate records while preserving the integrity of all associated clinical data.
The merge process is designed with both safety and usability in mind. Authorized administrators can access the merge functionality easily through Tamanu’s admin panel, using a simple user interface. Here they can review duplicate records and complete the consolidation process. The system preserves all medical history, appointment records, clinical notes, laboratory results, and other patient data, ensuring that no information is lost during the merge operation.
This comprehensive data preservation is crucial for maintaining clinical continuity and meeting regulatory requirements for medical record retention. The merged record provides clinicians with a complete, unified view of the patient’s healthcare history, enabling more informed clinical decision-making and better care coordination.
The merge tool also maintains an audit trail of the consolidation process, documenting which records were merged and when, supporting quality assurance efforts and regulatory compliance requirements.
Strategy 5: Database-Wide Reporting
Maintaining long-term database integrity requires periodic assessment and cleanup of existing patient data. Tamanu’s comprehensive reporting tool addresses this need by analyzing entire patient databases to identify potential duplicates that may exist within legacy data or have been missed by real-time detection systems.
The reporting system employs advanced pattern recognition algorithms to examine patient data across multiple dimensions, identifying subtle similarities that might indicate duplicate records. Like the real-time duplicate detection, this analysis goes beyond simple name matching to consider combinations of demographic information, contact details, and other identifying characteristics that could suggest the same individual is represented multiple times in the database. The system is also designed to improve as it goes. We leverage machine learning to enhance the identification of potential duplicate patient records. Our models are trained to account for regional naming variations and cultural nuances—for instance, recognizing that “Jenny” and “Jennifer” may refer to the same individual. This is done by labelling pairs of potential matches as duplicate, different or unsure. This approach improves accuracy across diverse datasets and geographies.
The reports provide actionable insights, presenting suspected duplicates in a format that enables efficient review and decision-making by administrative staff. This systematic approach to database maintenance helps healthcare organizations conduct regular data hygiene audits, ensuring ongoing database quality and supporting accurate healthcare analytics and reporting.
These periodic cleanups are particularly valuable for organizations transitioning from paper-based systems or consolidating data from multiple legacy electronicsystems, where duplicate creation may have occurred during data migration processes.

The Importance of Integrated Systems and Processes
While Tamanu’s built-in deduplication strategies provide robust protection against patient duplicates, the most effective approach to patient identity management can involve integration with complementary systems and processes that strengthen identification accuracy from multiple angles.
Biometric Identification Systems
Biometric identification represents a powerful complement to traditional patient identification methods, offering unique advantages in accurately distinguishing between individuals. Simprints, an open-source biometric identification platform, is one such example which exemplifies how these technologies can enhance patient identity management in healthcare settings.
Biometric systems capture unique physiological characteristics—such as fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial features—that remain consistent throughout an individual’s lifetime. When integrated with EMR systems like Tamanu, biometric identification can provide definitive patient verification that transcends the limitations of traditional identifiers like names, addresses, or even identity documents, which can be forgotten, lost, or shared between family members.
Simprints has demonstrated particular effectiveness in challenging healthcare environments, including refugee settings, rural communities, and populations with limited documentation. The system’s open-source nature makes it accessible to healthcare organizations with varying resource levels, while its offline capabilities ensure functionality in areas with limited connectivity—a critical consideration for many healthcare deployments.
Biometric identification is not a panacea – in larger populations across broad age and ethnic spectrums, biometrics can help to massively reduce patient duplication and improve patient identification, but the systems still need to be backed by strong patient management systems and high quality policies and procedures.
Civil Registration and Vital Statistics (CRVS) Integration
Civil Registration and Vital Statistics systems provide another crucial layer of patient identity verification and lifecycle management. These systems maintain authoritative records of births, deaths, marriages, and other vital life events that establish and track individual identities throughout their lives. EMRs should interact with CRVS systems at moments including birth and death to ensure that people have official identities that benefit them throughout all facets of their lives, not just healthcare. The integration of CRVS systems with EMRs like Tamanu creates a comprehensive identity ecosystem where healthcare records are anchored to officially recognized vital events.
Birth registration data helps establish definitive patient identities from the earliest stages of life, providing healthcare systems with authoritative information about patient demographics and family relationships. Death registration integration ensures that deceased patients are appropriately flagged in healthcare systems, preventing inappropriate record creation and supporting accurate population health statistics
OpenCRVS represents a leading example of modern CRVS implementation, working globally to improve the management of vital events and strengthen the foundation of identity management systems. Also a free and open-source platform, OpenCRVS are working in the Indo-Pacific region with partners including BES and agencies such as SPC. When integrated with healthcare systems, CRVS data provides several critical benefits for patient identity management.
Conclusion
Effective patient duplicate management requires a comprehensive, multi-layered approach that addresses both prevention and remediation while integrating with broader identity management ecosystems. Tamanu EMR’s five-strategy framework—PMI integration, ID card systems, real-time detection, merge tools, and database-wide reporting—provides healthcare organizations with robust tools for maintaining clean, accurate patient databases.
By combining Tamanu’s built-in deduplication strategies with thoughtful integration of complementary identification systems, healthcare organizations can achieve the highest levels of patient data integrity. This comprehensive approach ensures that every patient record is unique, accurate, and complete—supporting the delivery of safe, coordinated, and effective healthcare services.
Tamanu EMR’s comprehensive approach to duplicate management provides healthcare organizations with the tools and strategies needed to achieve and maintain this essential data quality standard. Come and chat with us about how our Project Management and Data teams can help your health ecosystem achieve its goals.
Watch our video on the five Tamanu deduplication strategies here:






